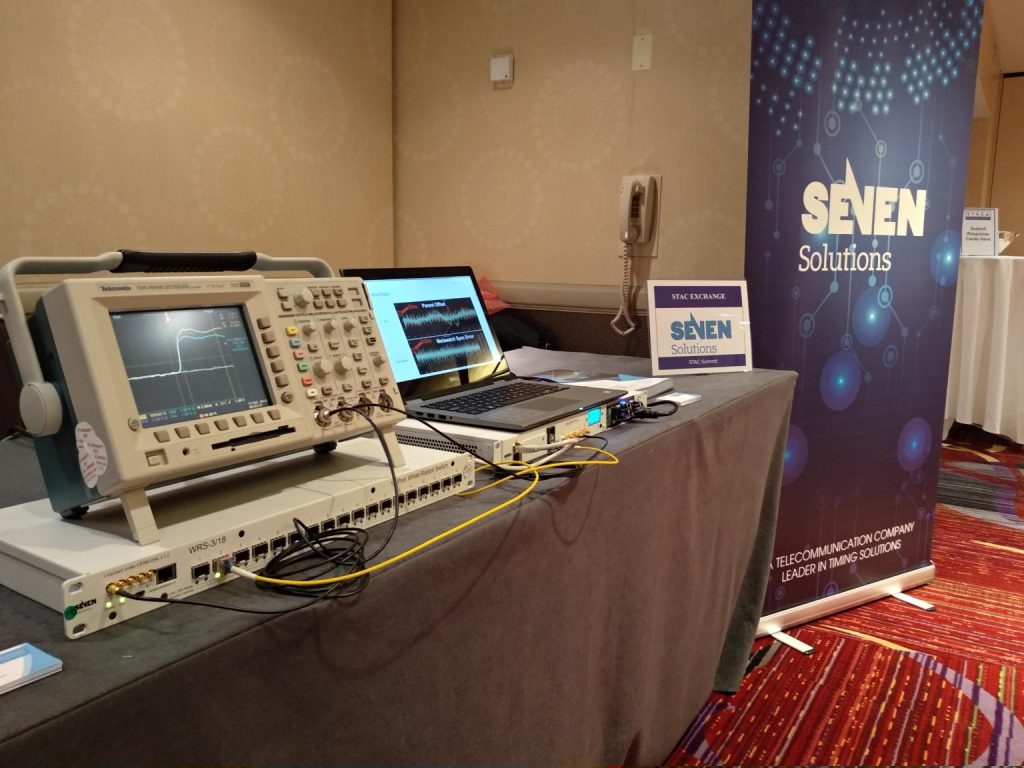
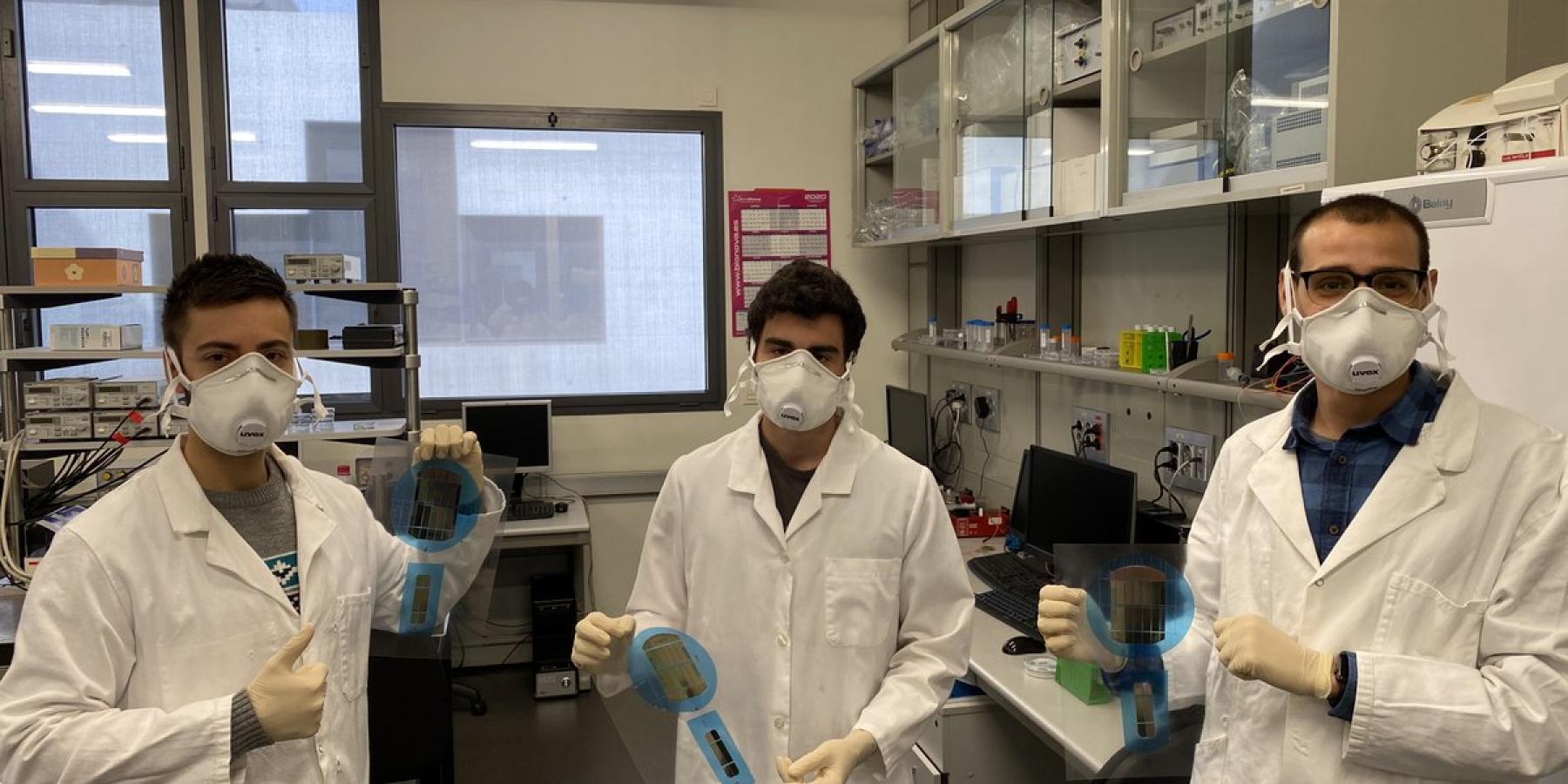
Space Giganet
The challenge of this industrial research project is to develop a competitive and highly innovative solution in the field of micro launcher avionics. The aerospace sector is a highly competitive market with few players, and KDPOF and Seven Solutions, promoters of the project, want to position themselves as suppliers of a network technology that combines the convergence of different criticality traffics with the flexibility and lightness of plastic fibre.
For some years now, the concept of Industry 4.0 has become increasingly apparent in the aerospace sector. This paradigm aims to simplify and streamline the processes that define an activity, appealing to all areas of industry and society. Among its fundamental pillars are connectivity, massive data processing, interoperability, and decentralisation of decision-making. In the aerospace sector, due to its intrinsic complexity and demanding requirements, digitisation is fundamental as a strategy to reduce the probability of accidents or failures, being an essential element to ensure safety and mission success. Other highly specialised and demanding sectors that can benefit from the results of this project are aeronautics and automotive.
The proposal is backed by relevant actors, such as PLD Space and GMV, who expect the results of the project to revolutionise the communications systems embedded in the different components of future micro-launchers.

Since space is a very complex environment, also in terms of communication networks, and characterised by large thermal variations, mechanical vibrations, microgravity, or presence of radiation, the specifications of communication systems are very complex and the optical systems composing the distributed network must be able to cope with the operational complexity. In this sense, communications systems based on plastic optical fibre (POF) are considered of great interest for space applications due to their characteristics such as their insensitivity to electromagnetic interference and the fact that they do not generate it, their resistance to mechanical stress (fibre twisting, micro, and macro bending), their lightness and their good behaviour in the face of vibrations. Since the publication of the IEEE 802.3bv 1000BASE-RH standard, a standard Ethernet-based POF communication solution is also available. With the degree of integration of today’s transceivers and the support of Energy Efficient Ethernet, this is achieved with the same or lower power consumption than copper-based solutions. Besides, the properties of plastic fibre, its high performance, and the resulting weight reduction make it possible to develop communication systems based on optimal solutions.

Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) technology improves bandwidth performance and solves the interoperability and reconfiguration problems of TTE and is low cost.
The communications network to be developed for future micro-launchers consists of six active two- and four-port systems forming two rings. This allows redundancy of the most critical traffic, meeting the reliability requirements of this type of application.
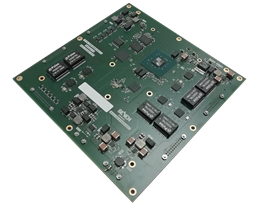
In this project, a time-sensitive network bridge (or TSN bridge) with four Gigabit Ethernet interfaces will be developed on a platform based on the Zynq-7030 MPSoC. Of the four interfaces, two will control 1000-Base-T compliant copper interfaces and two plastic optical fibre (1000-Base-RH). This design will, on the one hand, make it easier to compare the performance of TSN over plastic fibre with that currently available over copper. It will also make it possible to have equipment with a 1000-Base-T interface available for testing and to preserve interoperability.