SIARA Project
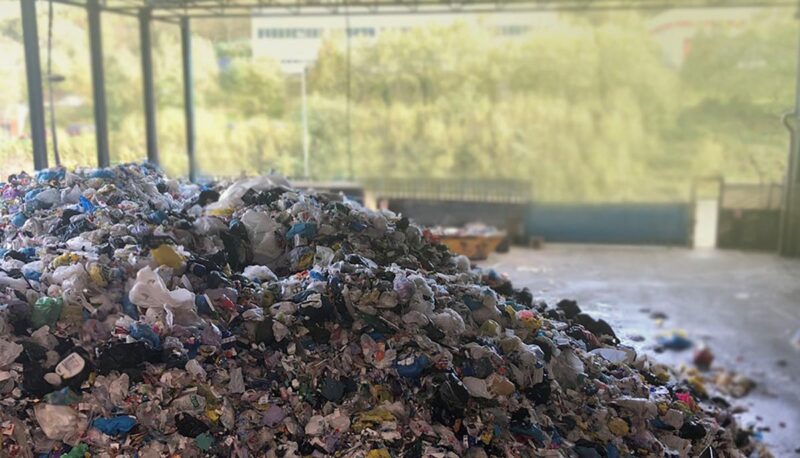
The SIARA project aims to respond to the needs of sorting plants for plastic packaging waste, cans and briks (from the yellow container) when removing bulky waste from the treatment line.
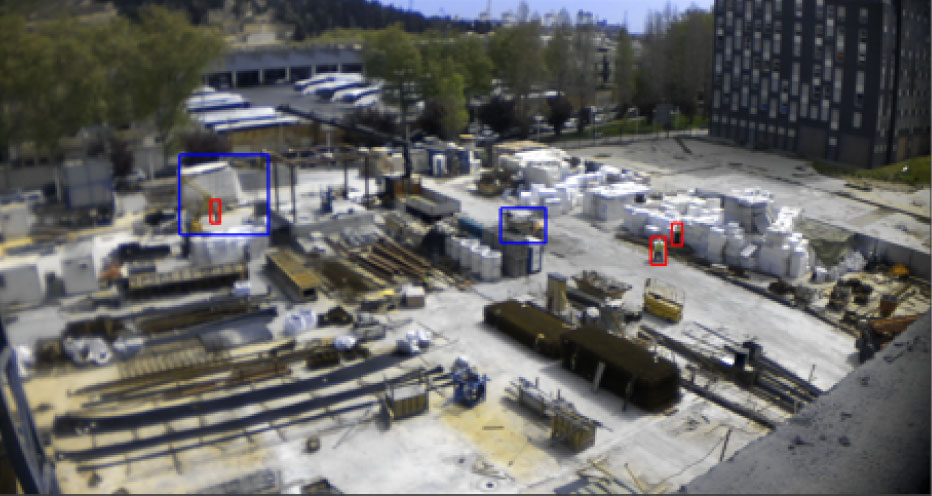
This is an artificial vision system based on deep learning (neural networks) for the detection and separation of bulky and heavy waste on the conveyor belt at the entrance of the sorting plant for plastic packaging waste, briks or cans, thus preventing the line from jamming or breaking down.
In addition, the project will improve other aspects such as process time, operation and maintenance costs and avoid tedious tasks for operators.
SIARA is an example of public-private collaboration in which Ecoembes, ATRIA, Mancomunidad de San Marcos, and Trinekens participate. It is financed by the Ministry of Economy and Business and co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF), whose objective is to strengthen socio-economic cohesion within the European Union by correcting the imbalances between its regions.
SIARA’s artificial vision will acquire data from the visible spectrum, multispectral and 3D cameras. And it will use deep learning to train its artificial intelligence system.

The system will learn to detect the waste that should not be removed and dispose of the rest through cameras with different sensors and an artificial intelligence system. Deep learning will train SIARA to create a database that will include image acquisition and tagging, a very important task that will be carried out during the early stages of the project.
Most machine vision applications use cameras that capture the visible spectrum, colours and textures, which will make it easier to distinguish plastics, boxes and cans that may have the same colour or texture. For further optimisation, the use of multispectral cameras will be explored. Similarly, 3D cameras will provide depth and can also help to pick out areas of waste on the conveyor belt in the image.
The SIARA project will lead to an increase in the recycling rate, efficiency of recycling plants and greater knowledge of the waste that Spanish citizens deposit in the yellow bin.
The test environment for the project is the sorting plant for plastic packaging, cans and boxes. The plant is managed by the Mancomunidad de San Marcos, where Trienekens operates.
Here, a conveyor belt receives the incoming waste and distributes it along the line in different selection and quality control processes of the selected materials. The acquisition system to be used for data capture will be installed on this conveyor belt and will take images of the waste entering the plant and will be calibrated in ATRIA‘s laboratories beforehand.